Cool Trivia: Did you know screens have so many categories? One of them even costs a million!

Last year, Samsung launched a 110-inch TV in the mainland market at a price of 1.04 million yuan (200k USD), using “self-luminous” MicroLED material.
Do you know what LCD, OLED, Micro LED, and mini LED are?
Well, we will ‘briefly’ discuss them today.
First of all, there is the LCD, which is the common liquid crystal panel.
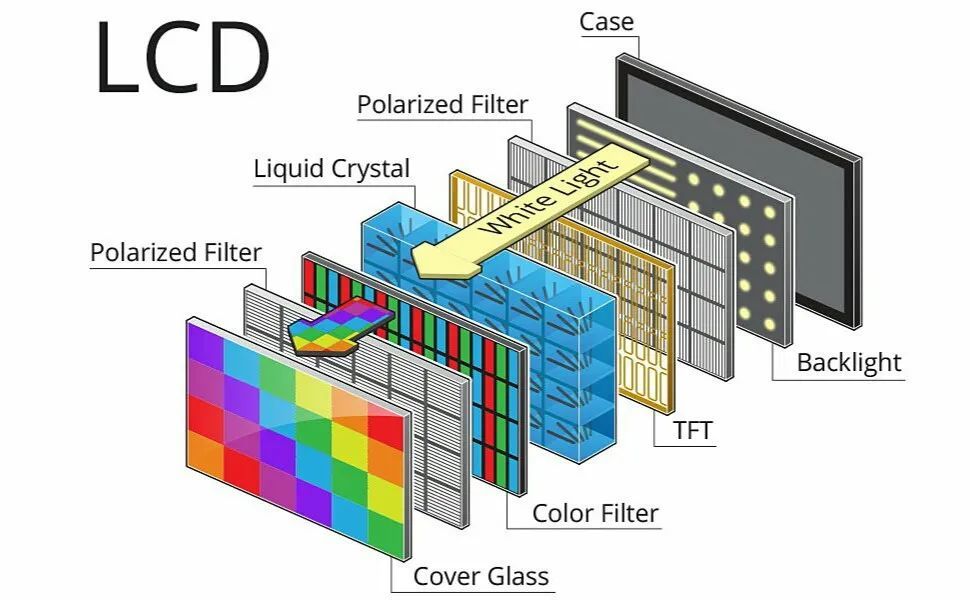
LCD, simply put, has three layers: the luminous backlight layer, the liquid crystal molecule layer that controls opening and closing, and the filter layer. After the LEDs in the light-emitting layer emit light, the passage of light is controlled by opening and closing the liquid crystal molecule layer. If light passes through, it will light up; if not, it will extinguish. After the light passes through, it will display the color of the filter; if it does not, it will be dark.
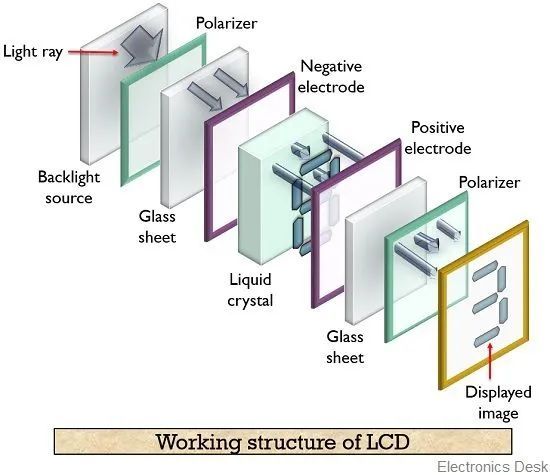
Since the color is controlled by the filter, and the LEDs in the bottom light-emitting layer only emit light, LCDs rarely experience “screen burn” issues (though not completely impossible).
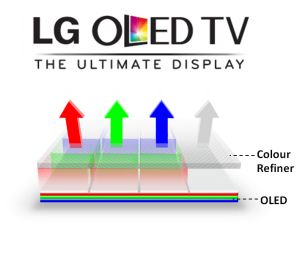
As for OLED, it’s simply the filter in the LCD that can emit light on its own once it’s powered up.
The material used here is organic.
These organic materials will emit light when electrically charged and completely extinguish when not.
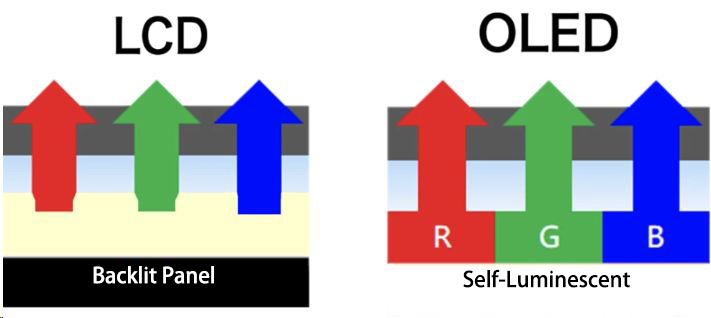
However, due to the differing light-emitting materials in these pixels, the wear and tear vary during use, making it easy for screen burn issues to occur. Additionally, the brightness of the OLED screen depends on the properties of these light-emitting materials.
As for mini LED, it’s a minor upgrade of the LCD.
Their principle is exactly the same as LCD’s, however, mini LED miniaturizes the backlight layer within it.
Mini LED uses smaller sized (200 microns) LED beads, which are zone-controlled to achieve light and dark zones, without needing the entire screen’s backlight layer to light up together.
It can maintain the excellent quality of LCD while achieving a contrast closer to that of OLED, essentially making the screen display blacker when it should be black. Additionally, since many small-sized beads are clustered in a certain area, the brightness of mini LEDs will be more concentrated and higher.
Micro LED, on the other hand, turns LCD almost into OLED.
The size of Micro LEDs’ light-emitting layer is at the μm level, directly corresponding one-to-one with the filter.
A Micro LED screen has as many independent light-emitting LEDs as its pixels, all of which can light up or turn off independently through chip control.
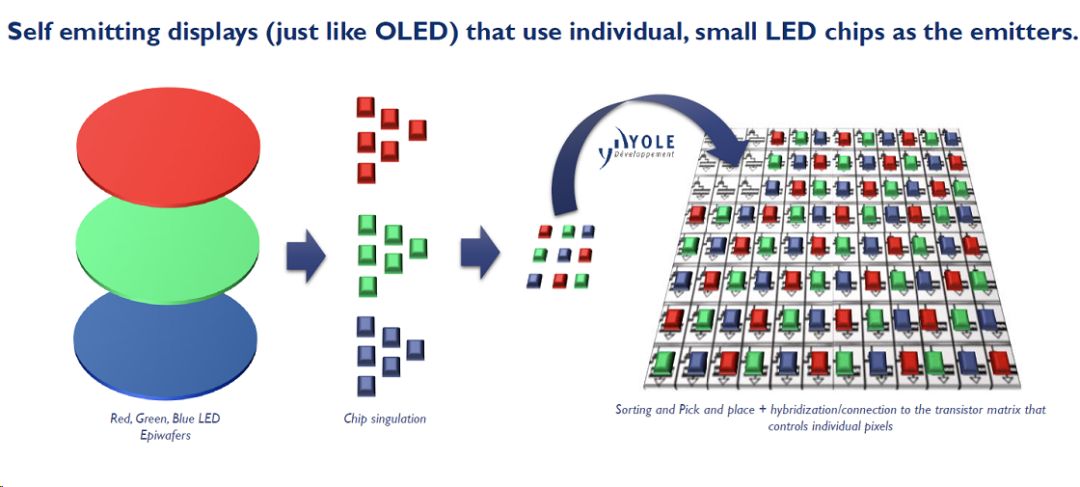
Since each pixel is individually controlled and emits light separately, manufacturers will promote Micro LED as a kind of “self-luminous” LED, just like how they present OLED.
However, OLEDs and Micro LEDs are fundamentally different — Micro LEDs use inorganic materials to emit light, not organic ones, so it will not lead to the aging of light-emitting molecules and colors.
It combines almost all the advantages of LCDs and OLEDs. It has high brightness, durability, contrast, and even lower power consumption.
However, Micro LED also has a very obvious shortcoming — it’s tough to produce.
Samsung’s first 110-inch Micro LED video wall is just at the 4K level. If it were OLED or LCD, Samsung would have gone for 8K long ago.
The more difficult the technology, the more expensive it naturally gets. So, this over one million yuan video wall is meant to showcase their technology prowess.
